Elimination mechanism reactivity examples Coordinate elimination e1cb activation unimolecular conjugate δe barrier Elimination unimolecular e1 reaction
E1 reaction
Mechanism elimination reactivity What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate E1 reaction elimination unimolecular
E1 energy diagram chapter elimination sn1 reactions substitution step nucleophilic alkyl halides iv stereochemistry che six unit ppt powerpoint presentation
E2 energy diagram reactionsEnergy diagram for e2 reactions E1 free energy diagramMechanism elimination alkyl halide where leaving concentration.
Elimination reaction : e1 and e2 reaction – examples, mechanismE1 reaction Free energy diagrams help free students from memorization – teach theEnergy e1 reaction potential coordinate diagrams sodium bromobutane following which represents transcribed text show hydroxide.

Reaction energy diagram
Energy e1 diagramElimination halides nucleophilic substitution alkyl wade sn1 reactions same carbocation Energy diagrams diagram memorization students help mechanism figureElimination reaction : e1 and e2 reaction – examples, mechanism.
Transition intermediate coordinate chemistrySolved based upon the following energy diagram, is this E1cb reaction coordinate elimination conjugate activationSn1 reaction energy diagram e2 reactions substitution cyclohexanes nucleophilic.

E1cb
Solved 13. which of the following potential energy diagramsEnergy diagram e2 reaction e1 upon following based elimination coordinate transcribed text show E1cbThe e1 reaction — master organic chemistry.
.


What is the Difference Between a Transition State and an Intermediate

E1cB - Elimination (Unimolecular) Conjugate Base
Reaction Energy Diagram - SN1 - YouTube

Elimination reaction : E1 and E2 reaction – Examples, Mechanism

PPT - Chapter 6 Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and

E1cB - Elimination (Unimolecular) Conjugate Base

E1 reaction

Elimination reaction : E1 and E2 reaction – Examples, Mechanism
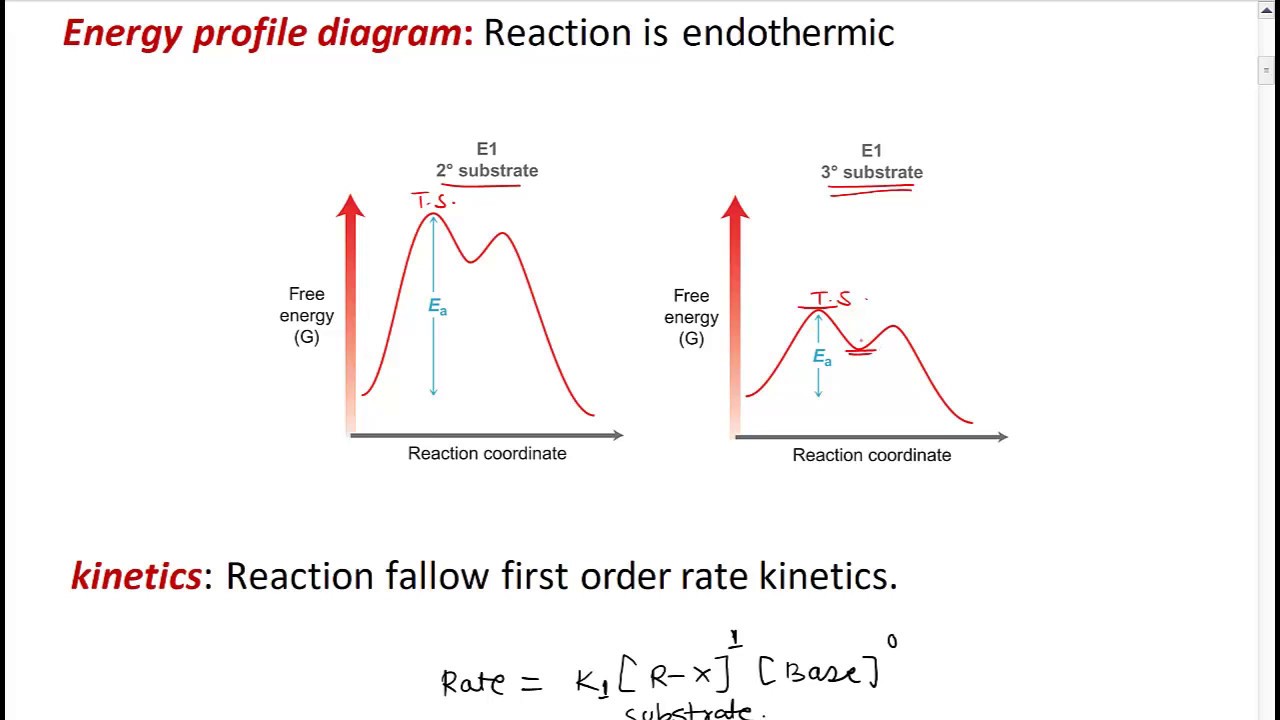
Elimination unimolecular E1 reaction - YouTube
